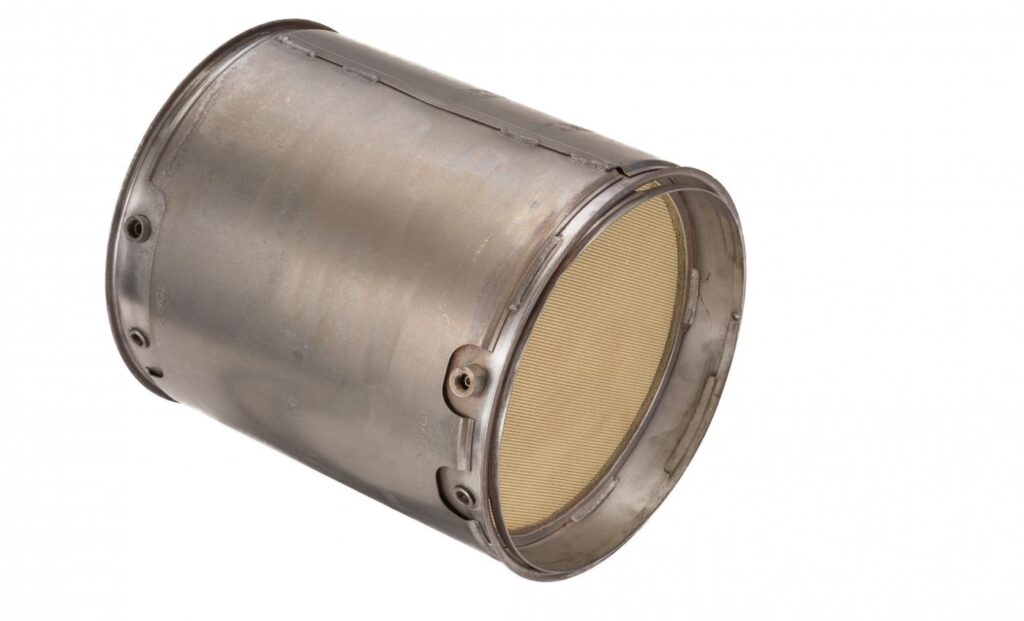
A diesel particulate filter, or DPF for short, is a device designed to capture and trap the harmful particles that are emitted from diesel engines.
When diesel fuel is burned, it creates tiny particles of soot and other materials that are released into the air through the exhaust system. These particles can be dangerous to human health and the environment, as they can cause respiratory problems and contribute to air pollution.
A DPF works by capturing these particles and storing them in a filter. The filter is made up of tiny passages that allow the exhaust gases to pass through while trapping the particles. Over time, the filter becomes filled with these particles, which can reduce the engine’s performance and fuel efficiency.
To prevent this, the DPF periodically goes through a process called regeneration. During regeneration, the filter is heated up to a very high temperature, which burns off the trapped particles and clears the filter.
DPFs require a lot of maintenance and upkeep. They are a common source of many of the most common fault codes, not to mention engine derates.
OEM software is the preferred method of diagnosing and working on DPF related issues:
Cummins Engines = Cummins Insite
Paccar MX Engines = Paccar Davie 4
Detroit Engines = Detroit Diagnosticlink
Isuzu Engines = Isuzu IDSS
In summary, a diesel particulate filter is a device that captures harmful particles from diesel engine exhaust and prevents them from being released into the air. It is an important component in reducing air pollution and protecting human health.
Keep an eye on this space, we will be publishing many more introductory articles that cover the basics regularly.